BALLOON FRAME E PLATFORM FRAME
BALLOON FRAME E PLATFORM FRAME
- 10 Lug 2022
La tecnologia costruttiva nota come “Balloon Frame” (di seguito BF), sviluppatasi negli Stati Uniti a partire dalla metà dell’Ottocento, è un sistema edilizio che prevede l’uso di sottili travi in legno poste in opera tramite chiodatura a costituire pareti, pavimenti e coperture di un fabbricato, cioè la struttura portante dello stesso, successivamente rivestita sia internamente che esternamente da uno strato di tavole che contribuisce alla rigidezza (Fig. 1 – immagine a sinistra).
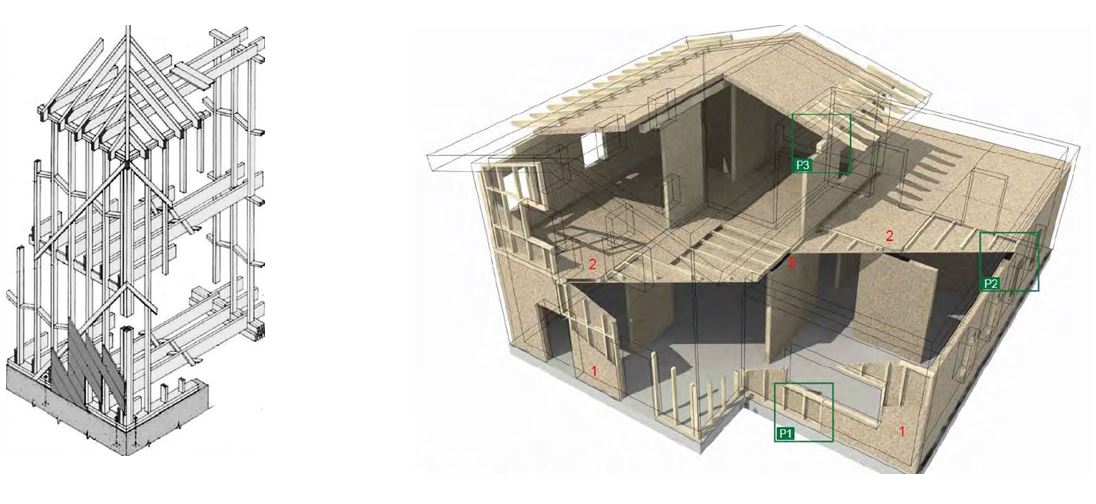
Fig. 1
Nello specifico, si utilizzano montanti leggeri e di lunghezza corrispondente all’altezza del fabbricato (tipicamente di due piani), posti in opera senza interruzione dal piano terreno alla copertura, chiodando sugli stessi una tavola a metà altezza (per un edificio di due piani) per la realizzazione del piano superiore.
Di seguito le principali caratteristiche di tale sistema costruttivo:
- elementi in legno di dimensioni standard e quindi adatti ad una produzione in serie, con taglio e numerazione in segheria, quindi invio in cantiere unitamente ad una dotazione di chiodi, nonchè porte e finestre già predisposte per il montaggio;
- leggerezza della struttura;
- velocità di montaggio;
- buone caratteristiche di coibentazione termica per la presenza delle intercapedini tra i tavolati , nonché sostanziale assenza di ponti termici.
Nel periodo compreso tra gli anni 20-30 del Novecento, venne sviluppato un nuovo sistema costruttivo a base lignea, noto come “Platform Frame” (di seguito PF), attualmente molto usato, con gli opportuni aggiornamenti tecnologici, in particolare negli Stati Uniti ed in Canada.
L’edificio PF (Fig. 1 – immagine a destra) ha una struttura portante a telaio, tipicamente in legno lamellare, con isolante termoacustico interposto e un ulteriore strato di isolamento esterno (cappotto). Le finiture esterne ed interne possono essere ad intonaco ma anche in doghe/pannelli in legno.
Le pareti sia esterne che interne sono generalmente così costituite (Figg. 2 e 3):
- telai formati da travi in legno lamellare impregnate in autoclave con sali ecologici, sezione minima 80 x 160 mm, poste verticalmente ad interasse non superiore a 60 cm;
- pannelli in legno OSB (Oriented Strand Board) posti internamente ed esternamente ai telai ed ad irrigidimento degli stessi.
Le pareti vengono realizzate ed assemblate industrialmente e poste in opera in cantiere.
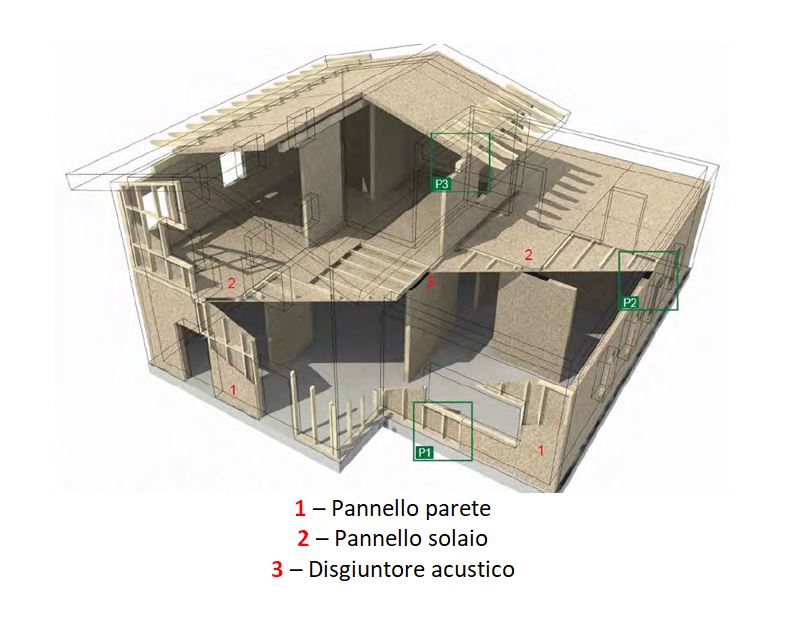
Fig. 2
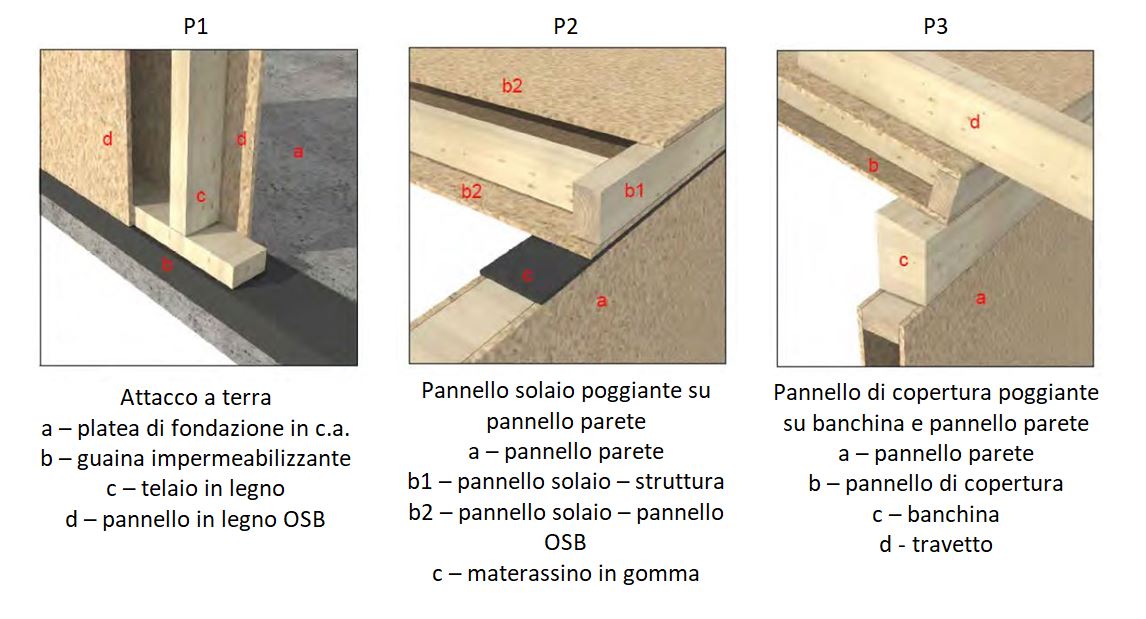
Fig.3
Fonti:
“Tecnologia delle costruzioni” – Ing. Marco Palazzuoli – Università di Pisa
“Seminario “Tecnica costruttiva” – Politecnico di Bari
 Ing. Fabio Di Matteo – ZED PROGETTI srl
Ing. Fabio Di Matteo – ZED PROGETTI srl
The construction technology known as “Balloon Frame” (hereinafter referred to as BF), developed in the United States since the mid-nineteenth century, is a building system that involves the use of thin wooden beams installed by nailing to form walls, floors and roofs of a building, i.e. the supporting structure of the same, then covered both internally and externally by a layer of boards that contributes to rigidity (Fig. 1 – image on the left).
Specifically, light uprights of length corresponding to the height of the building (typically of two floors) are used, installed without interruption from the ground floor to the roof, nailing on them a board at half height (for a two-storey building) for the construction of the upper floor.
The main characteristics of this construction system are as follows:
– standard size wooden elements suitable for mass production, with cutting and numbering in the sawmill, then sending to the site together with a set of nails, as well as doors and windows already prepared for installation;
– lightness of the structure;
– speed of assembly;
– good thermal insulation features due to the presence of interspaces between the boards, as well as substantial absence of thermal bridges.
In the period between the 20s and 30s of the twentieth century, was developed a new construction system based on wood, known as “Platform Frame” (hereinafter PF), currently widely used, with appropriate technological updates, especially in the United States and Canada.
The PF building (Fig. 1 – image on the right) has a load-bearing frame structure, typically in laminated wood, with interposed thermal-acoustic insulation and an additional layer of external insulation (coat). The external and internal finishes can be plastered but also in wooden slats/panels.
Both external and internal walls are generally made up as follows (Figs. 2 and 3):
– frames made of glulam beams impregnated with ecological salts in an autoclave, minimum section 80 x 160 mm, installed vertically at a distance of no more than 60 cm.
– OSB (Oriented Strand Board) wooden panels placed inside and outside the frames and stiffening them.
The walls are made and assembled industrially and placed on site.

