LO STANDARD IPMS PER LA MISURAZIONE DI EDIFICI AD USO INDUSTRIALE
International Property Measurement Standards: Industrial Buildings
- 12 Apr 2020

Dopo l’articolo “LO STANDARD IPMS PER LA MISURAZIONE DI EDIFICI AD USO UFFICIO”, continuiamo la trattazione prendendo in considerazione la misurazione degli edifici industriali
Lo standard IPMS per la misurazione delle unità immobiliari è stato creato allo scopo di rendere unico il sistema di misurazione delle unità, in modo tale da poter rendere leggibile i dati a livello internazionale. L’International Property Measurement Standards Coalition (IPMSC) è stata costituita il 30 maggio 2013 dopo essersi incontrata presso la Banca Mondiale a Washington DC. La finalità è di realizzare l’armonizzazione degli standard nazionali di misurazione della proprietà attraverso la creazione e l’adozione di standard internazionali concordati per la misurazione degli edifici.
Questo documento per la misurazione degli edifici industriali è il terzo standard di classe di costruzione preparato dal Comitato per la Definizione degli Standard della Coalizione (SSC).
In merito al “IPMS: Edifici ad uso Industriale”, sono stati definiti 4 standard
- IPMS 1 – standard per la misurazione dell’area complessiva degli Edifici, per attività di pianificazione o per la stima dei costi di costruzione e che è assunto valido per tutte le categorie di edifici.
- IPMS 2 – Industrial è stato sviluppato per misurare le aree interne di un complesso industriale edificio e, con l’uso delle Aree dei Componenti, aiuterà l’industria immobiliare a fare un uso efficiente dello spazio e per dati di riferimento.
- IPMS 3A – Industrial e IPMS 3B – Industrial usati per misurare i settori di occupazione esclusiva per le transazioni e altri scopi. La SSC ha identificato due diverse basi di misura, necessarie per soddisfare le esigenze del mercato globale per la misurazione delle aree in occupazione esclusiva.
Ci sono delle definizioni di base che riguardano gli elementi trattati.
Definizioni
- Altezza Interna – L’altezza all’interno di un Edificio o sezione di un Edificio, misurata dal pavimento al punto più basso di un soffitto, ignorando l’esistenza di eventuali staffe, montanti o fissaggi e raccordi.
- Altezza Netta – L’altezza all’interno di un Edificio o sezione di un Edificio misurata dal pavimento al punto più basso dell’elemento strutturale di copertura, ignorando l’esistenza di staffe, montanti o fissaggi e raccordi.
- Area Ausiliare – Un’area ad uso esclusivo, che è staccata dall’area principale misurata o viene utilizzata per scopi supplementari.
- Area di carico – Aree progettate per l’accesso dei veicoli vicino a una Piattaforma di Carico.
- Area del Pavimento – L’area di una struttura normalmente orizzontale, permanente, portante per ogni livello di un edificio.
- Area Riparata – Qualsiasi parte della Superficie Coperta non completamente chiusa, ma escluse le aree insignificanti sotto le grondaie.
- Balaustra – Barriera protettiva formata da una parete solida, ringhiere o altre strutture.
- Balcone – Una piattaforma esterna al piano superiore con una balaustra ai lati aperti sporgente o incassata da un muro esterno e che include in questa definizione, terrazze panoramiche generalmente accessibili, gallerie esterne e logge.
- Coalizione – Gli Amministratori della IPMS, che comprendono organizzazioni senza scopo di lucro, ciascuna con un mandato di interesse pubblico.
- Componente – Uno degli elementi principali in cui la Superficie del Pavimento di un edificio può essere suddiviso.
- Edificio – Struttura indipendente collegata o distaccata che forma tutta o parte di una proprietà.
- Edificio Industriale – Un edificio utilizzato principalmente per scopi industriali come la produzione e il magazzino, indipendentemente dal fatto che una parte dell’edificio sia utilizzata o meno per altri scopi.
- Esperto nella Misurazione degli Spazi – Un Fornitore di Servizi qualificato per esperienza o formazione a misurare Edifici in conformità con lo standard IPMS.
- Faccia Dominante Interna (FDI) – La superficie interna comprendente più del 50% dei primi 2,75 metri misurati verticalmente dal pavimento, o al soffitto se di altezza inferiore, per ogni Sezione di Parete FDI. Se ciò non si verifica, la superficie finita è considerata l’FDI.
- Fornitore di Servizi – Qualsiasi entità che fornisce consulenza immobiliare a un Utente o a Terzi, inclusi, a titolo esemplificativo ma non esaustivo, Valutatori, ispettori, gestori di strutture, gestori di proprietà, asset manager, agenti e mediatori, Esperti nella Misurazione degli Spazi, consulenti di costi, progettisti di interni e architetti.
- Industria Immobiliare – Comprende Utenti, Fornitori di Servizi e Terzi.
- IPMS – Standard internazionali di misurazione della proprietà.
- IPMSC – L’International Property Measurement Standards Coalition.
- IPMS 1 – Il totale delle superfici di ogni piano di un Edificio misurate al perimetro esterno dei Muri Esterni, Aree Coperte e Balconi.
- IPMS 2 – Il totale delle superfici di ogni piano di un Edificio misurate alla Faccia Dominante Interna di tutti i Muri Esterni e Balconi su ogni piano.
- IPMS 3 – La Superficie del Pavimento disponibile in esclusiva per un occupante.
- Mezzanino – Un piano intermedio o parziale, diverso da una Passerella, che di solito è completamente o parzialmente aperto su uno o più lati.
- Patio – Una terrazza lastricata o pavimentata, adiacente un Edificio, che può essere coperto da una struttura indipendente.
- Parete Esterna – L’elemento di inclusione di un Edificio, comprese le finestre e le pareti, che separa l’area esterna dall’area interna.
- Passerella – Una passerella interna o esterna sopra l’area circostante che fornisce un accesso al livello superiore.
- Piattaforma di Carico – Piattaforme elevate all’apertura di un edificio progettate per la ricezione o la spedizione di merci o attrezzature.
- Proprietà – Qualsiasi risorsa immobiliare nell’ambito edilizio.
- Sezione di Parete della FDI (faccia dominante interna) – L’estensione di ogni sezione di un muro esterno in cui la superficie interna finita di ogni parte di una finestra, muro o altre caratteristiche costruttive esterne varia dalla superficie interna finita adiacente della finestra, parete o caratteristica costruttiva esterna, ignorando l’esistenza di eventuali colonne.
- SSC – Il Comitato per la definizione degli standard nominato dall’IPMSC per sviluppare standard globali per la misurazione delle proprietà.
- Struttura – Una costruzione che fornisce un riparo o svolge una funzione accessoria, ma non è necessariamente completamente chiusa.
- Strutture Comuni – Quelle parti di un edificio che, in più occupazioni, fornirebbero strutture condivise che in genere non cambiano nel tempo e possono includere, ad esempio, aree di circolazione, scale, scale mobili, ascensori/ascensori, locali con motori, toilets, armadi per addetti alle pulizie, locali per impianti, aree di rifugio antincendio, locali di manutenzione e parcheggi non assegnati.
- Strutture Standard – vedi Strutture Comuni.
- Struttura Temporanea – Un elemento fisico all’interno di un edificio installato a titolo provvisorio o permanente, la cui rimozione non danneggerebbe l’integrità fisica dell’Edificio.
- Superficie dei Componenti – La totale Superficie del Pavimento attribuita a uno dei Componenti.
- Superficie Coperta – L’estensione della superficie di un Edificio coperto da uno o più tetti e il cui perimetro è talvolta indicato come la linea di gocciolamento, essendo l’estensione strutturale permanente più esterna, escluse le sporgenze ornamentali.
- Superficie Finita – La superficie della parete direttamente sopra l’incrocio orizzontale parete-pavimento, ignorando battiscopa, canaline per cavi, unità di riscaldamento e raffreddamento e tubazioni.
- Terzo – Qualsiasi entità diversa da un Utente o da un Fornitore di Servizi con un interesse nella misurazione di proprietà, includendo, ma non limitatamente a questi, governi, banche, altri enti finanziatori di proprietà, analisti di dati e ricercatori.
- Utente – Un proprietario-occupante, promotore, investitore, acquirente, venditore, proprietario o affittuario.
- Valutatore – Un Fornitore di Servizi con un’adeguata qualifica professionale in materia di valutazione o perizia.
- Veranda – Un’area aperta o parzialmente chiusa all’esterno di un Edificio a livello del suolo (livello 0) e coperta da un tetto che è parte integrante dell’Edificio.
Scopo e campo di applicazione delle norme
Scopo delle norme
L’obiettivo dell’IPMS è quello di fornire trasparenza nella misurazione degli Edifici. L’IPMS supporta le richieste dei Fornitori di Servizi, dei Terzi e degli Utenti della Proprietà per la coerenza nel riportare la misura. Finora l’area di superficie dichiarata in edifici identici varia notevolmente da un paese all’altro e talvolta all’interno dello stesso paese, a causa delle diverse convenzioni di misura.
Le misurazioni possono essere utilizzate per la gestione patrimoniale, il confronto, la costruzione, il facility management, il marketing, il finanziamento immobiliare, la ricerca, la transazione, la valutazione e altri scopi.
Uso degli Standard
IPMS definisce cosa deve essere misurato in un Edificio e i parametri di misura. L’IPMS non detta come devono essere ottenute o utilizzate le misurazioni.
Lo standard IPMS appropriato (come ad esempio ufficio, residenziale, industriale, commerciale) da utilizzare deve essere scelto in base alla funzione attuale o proposta dell’Edificio o della parte di Edificio da misurare.
L’IPMS può essere utilizzato per qualsiasi scopo concordato tra gli Utenti, i Fornitori di Servizi e Terzi.
L’IPMS fornisce un linguaggio comune che può interfacciarsi con gli standard di misura locali esistenti.
Accuratezza
I Fornitori di Servizi devono adottare processi di misurazione e di calcolo adeguati a soddisfare le esigenze degli Utenti. Tali requisiti possono variare da un’ampia approssimazione per alcuni scopi ad un calcolo preciso per motivi contrattuali o di altro tipo.
Designazione del livello del pavimento
Il SSC ha riscontrato che non vi è coerenza di mercato nel riferimento ad un determinato livello.
Per tutte le classi di proprietà IPMS ha adottato il livello 0 come livello di base primario. I livelli superiore e inferiore sono indicati in sequenza come il numero di livelli superiori o inferiori al livello 0. Ad esempio, i livelli 1, 2 o 3, ecc. sono superiori al livello 0 e i livelli -1, -2 o -3, ecc. sono inferiori a Livello 0.
Criteri Generali di Misurazione e Calcolo
- L’immobile deve essere misurabile.
- La misurazione deve essere verificabile secondo criteri oggettivi.
- Tutte le misure, ad eccezione delle altezze, devono essere prese orizzontalmente.
- Le misurazioni e i calcoli devono essere chiaramente documentati, precisando le seguenti informazioni:
- Lo standard IPMS adottato, ad es. IPMS 1, IPMS 2 – Industriale o IPMS 3A – Industriale o IPMS 3B – Industriale
- Il criterio utilizzato per la misurazione
- L’unità di misura
- La tolleranza di misurazione
- La data di misurazione.
- Gli Edifici devono essere misurati individualmente e riportati piano per piano come esistenti o proposti al momento della misurazione.
- I principi dell’IPMS devono essere estrapolati utilizzando un approccio basato sul buon senso.
Buona pratica di misurazione
- Generale – L’SSC raccomanda di accompagnare tutte le misurazioni IPMS con disegni CAD (computer-aided design) o dati BIM (building information modelling), ma laddove vengano utilizzati altri disegni come base di misurazione, sarà preferibile impiegare le dimensioni indicate sui disegni anziché affidarsi soltanto a quelle rilevate con la misurazione. Il Fornitore di Servizi deve esplicitare le modalità di determinazione della Superficie di Pavimento, ad esempio sulla base di disegni CAD, altri disegni o mediante misurazione con laser o nastro metrico.
- Unità di misura – Misurazioni e calcoli devono essere effettuati nelle unità di misura comunemente adottate nel rispettivo Paese. Utenti e Terzi possono richiedere di convertire le misurazioni: in tal caso è necessario indicare il fattore di conversione.
- Rapporti di misurazione – Qualsiasi Superficie dei Componenti in IPMS 1 o IPMS 2 segnalata ad un Utente o a Terzi dovrebbe, ove possibile e ove opportuno, essere riferita ad un disegno e ad un foglio di calcolo della Superficie del Componente opportunamente colorato. Nel riportare le misurazioni e le aree di piano per gli sviluppi proposti, i Fornitori di Servizi devono prestare particolare attenzione a garantire che le misurazioni siano referenziate in modo incrociato con la massima accuratezza possibile rispetto ai progetti alla data del report.
- Aree di utilizzo limitate – I Fornitori di Servizi devono essere consapevoli del fatto che in alcuni mercati ci possono essere aree degli edifici che non possono essere occupate in modo legale o effettivo a causa della legislazione locale o nazionale. Tali aree e i loro limiti devono essere identificati, misurati e dichiarati separatamente all’interno delle aree segnalate IPMS. Se le aree sono soggette a restrizioni, ciò deve essere dichiarato nel documento di segnalazione e in qualsiasi foglio di calcolo della Superficie die Componenti. Gli Utenti e i Terzi devono essere consapevoli che l’inclusione delle aree misurate nell’IPMS non significa necessariamente che le aree siano disponibili per l’occupazione o l’uso legale. Deve essere indicato il motivo per cui una particolare area è considerata come Area ad uso limitato. Gli esempi che seguono non sono esaustivi:
- Esempio 1 – Differenza di area rispetto alla Faccia Dominante Interna. Potrebbe essere necessario mostrare la differenza, se del caso, nell’area del pavimento tra le misurazioni effettuate sulla faccia dominante interna e le misurazioni effettuate sulla giunzione parete-pavimento.
- Esempio 2 – Aree con restrizioni di altezza
In vari mercati, le aree definite di altezza limitata o limitata sono identificate separatamente. Tale altezza può variare da una giurisdizione all’altra e in alcuni casi l’altezza limitata può essere dovuta a caratteristiche costruttive. - Esempio 3 – Aree con luce naturale limitata
In alcune giurisdizioni, le aree con luce naturale limitata in un Edificio devono essere identificati separatamente. - Esempio 4 – Sopra e sotto terra
Un Edificio è generalmente composto da piani fuori terra e piani interrati. Ai fini della misurazione, questa distinzione può essere importante per determinare le condizioni in cui i locali possono essere utilizzati in conformità con la legislazione locale o nazionale, alle norme sull’idoneità all’abitazione o alla tassazione.
- Adeguamento tra IPMS e altri standard
In caso di adozione del dual reporting, la corrispondenza tra l’IPMS e lo standard a cui si fa riferimento deve essere adeguatamente spiegata. Il SSC raccomanda ai membri della Coalizione di fornire una guida di interfaccia nelle loro procedure di implementazione locale per i rispettivi membri.
Standard IPMS
Gli standard IPMS (e i loro principali utilizzi) sono:
– IPMS 1 (Esterno)
– IPMS 2 – Industriale (interno)
– IPMS 3A – Industriale (esterno: occupazione esclusiva)
– IPMS 3B – Industriale (interno: occupazione esclusiva).
IPMS 1 – Industriale
Utilizzo – L’IPMS 1 è utilizzato per misurare l’area di un Edificio, comprese le pareti esterne. L’intento primario dell’IPMS 1 è quello di essere utilizzato per scopi di pianificazione o per il calcolo sommario dei costi delle proposte di sviluppo. L’IPMS è la misura dell’intero edificio.
Definizione – IPMS 1: Il totale delle superfici di ogni livello di piano di un Edificio misurato al perimetro esterno delle Pareti Esterne, delle Aree Riparate e dei Balconi. La definizione per IPMS 1 è la stessa per tutte le classi di Edifici. In molti mercati, ma non universalmente, questa è conosciuta come Area Esterna Lorda.
Pratica di misurazione – Le aree per l’IPMS 1 devono essere prese da disegni o in loco. Se necessario, l’IPMS 1 può essere riportato Componente per Componente per ogni piano di un Edificio. La somma delle Superfici dei Componenti deve essere uguale all’IPMS 1. Se non ci sono disegni disponibili per un seminterrato, l’area deve includere una stima dello spessore delle pareti esterne. Per quanto riguarda le Aree Riparate, l’IPMS 1 deve essere misurato all’Area Coperta. Per quanto riguarda le tapparelle e altre aperture, per misurare l’IPMS 1 si deve seguire la linea perimetrale esterna principale dell’edificio che attraversa tali aperture.
Balconi e Mezzanini devono essere misurati fino al bordo esterno della costruzione del pavimento.
Inclusioni – L’IPMS 1 comprende tutte le aree e le pareti, le colonne e i passaggi o passaggi chiusi tra edifici separati, disponibili per uso diretto o indiretto. Le aree vuote chiuse, come gli atri, sono incluse solo al livello più basso del pavimento.
Misure incluse ma da indicare separatamente -Balconi, Aree Riparate, Verande e Mezzanini sono inclusi, ma la misura di ciascuno di essi deve essere dichiarata separatamente.
Misure escluse ma da indicare separatamente – La misura per IPMS 1 non comprende:
– Strutture temporanee
– Pozzi di luce aperti o i vuoti del livello superiore di un atrio
– Scale esterne aperte che non sono parte integrante dell’Edificio, ad esempio, una scala antincendio a struttura aperta
– Qualsiasi struttura al di fuori dell’area coperta.
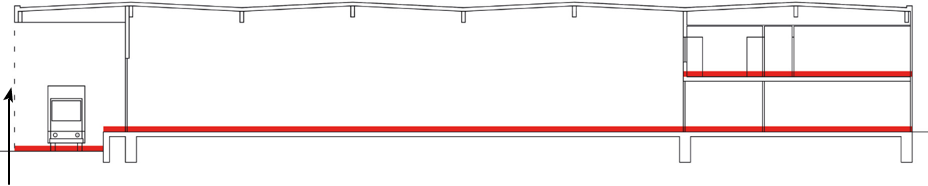
Diagramma 1: IPMS 1 – Superficie Totale del Pavimento a Liv. 0 e Liv. 1
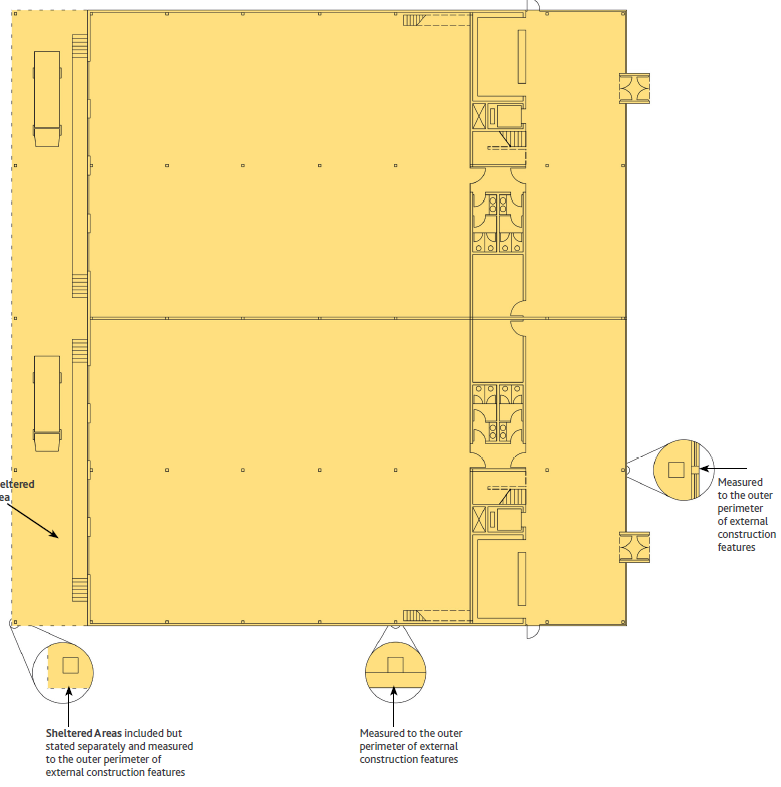
Diagramma 2: IMPS 1 Piano Terra (Liv. 0)
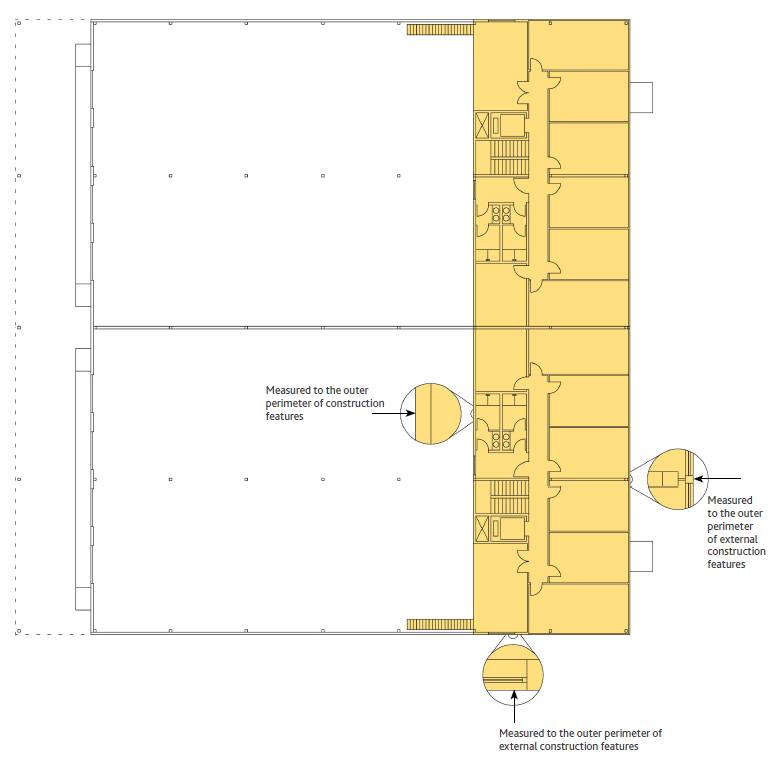
Diagramma 2: IMPS 1 Piano Sup. (Liv. 1)
IPMS 2 – Industriale
Utilizzo – IPMS 2 – Industrial è una misura dell’intero Edificio che viene usata per misurare l’area di confine interno di un Edificio. L’uso primario previsto è quello di fornire dati sull’uso dello spazio e per il confronto. IPMS 2 – Industrial consente agli Utenti, ai Terzi e ai Fornitori di Servizi di effettuare confronti diretti tra i dati derivanti da diverse pratiche di mercato.
Definizione – IPMS 2 – Industriale è Il totale delle superfici di ogni livello di piano di un edificio misurato alla Faccia Dominante Interna di tutte le pareti esterne e dei balconi su ogni livello.
In molti mercati, ma non universalmente, questo è simile all’area interna lorda.
Pratica di misurazione – Tutte le aree di un Edificio industriale, inclusi ad esempio gli uffici, devono essere misurati in conformità con l’IPMS 2 – Industriale.
Balconi e Mezzanini devono essere misurati fino alla faccia interna della balaustra, ma non oltre il bordo esterno della costruzione del pavimento.
Se richiesto, l’IPMS 2 – Industriale può essere riportato Componente per Componente per ogni piano di un Edificio.
Inclusioni – IPMS 2 – Industriale include tutte le aree interne, comprese le pareti interne e le colonne. Le aree vuote chiuse, come gli atri, sono incluse solo al livello più basso del piano.
Misure incluse ma da indicare separatamente – Balconi, Aree di Carico interne, Mezzanini e passerelle o passaggi chiusi tra Edifici separati, disponibili per uso diretto o indiretto, sono inclusi ma la misura di ciascuno di essi deve essere dichiarata separatamente.
Misure escluse ma da indicare separatamente – Le aree al di fuori della Parete Esterna, come le aree riparate e le Aree di Carico esterne, non devono essere misurate, ma se vengono misurate, queste aree devono essere dichiarate individualmente e separatamente.
Le Aree Riparate devono essere misurate alla superficie finita di qualsiasi parete e altrimenti al perimetro esterno dell’area coperta.
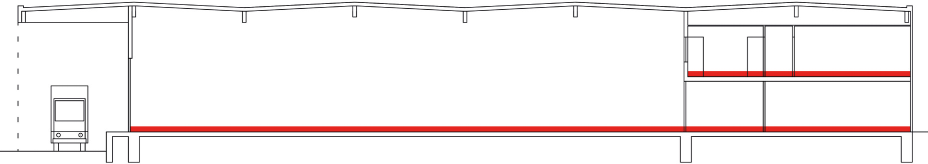
Diagramma 4: IPMS 2 Industriale – Superficie Totale del Pavimento a Liv. 0 e Liv. 1
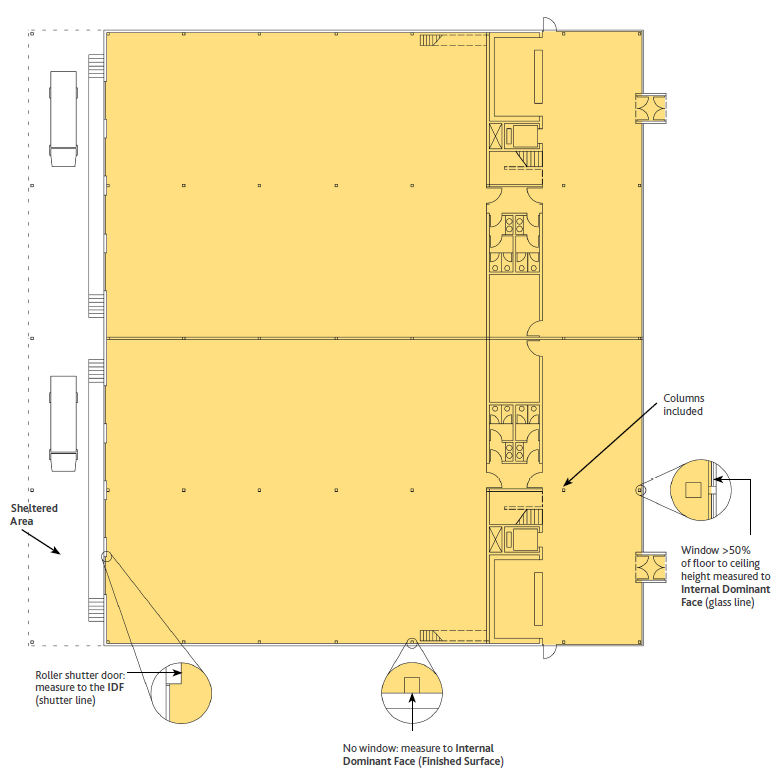
Diagramma 5: IMPS 2 Piano Terra (Liv. 0)
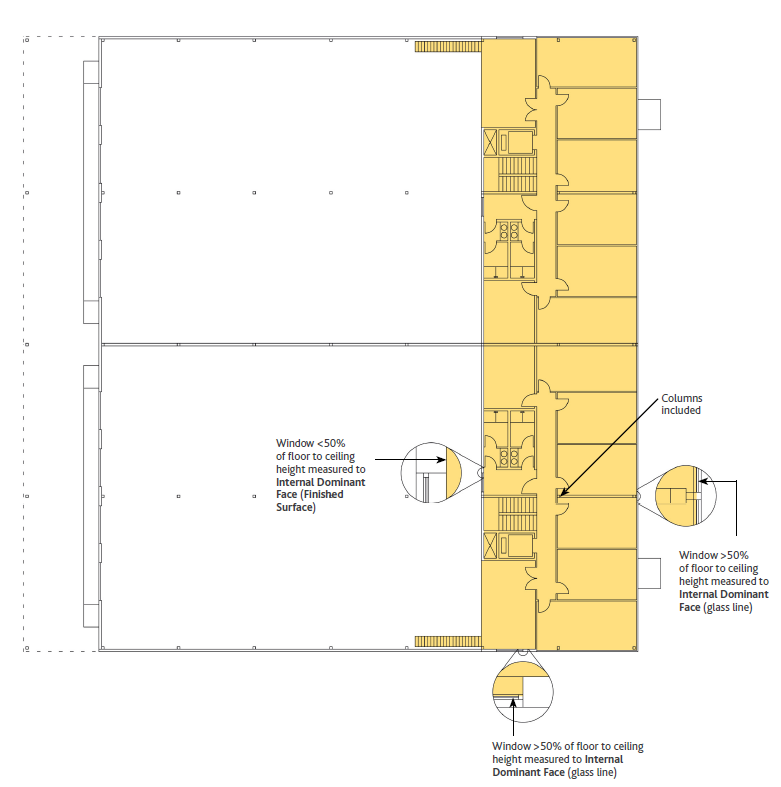
Diagramma 6: IMPS 2 Piano Sup. (Liv. 1)
IPMS 3 – Industriale
Utilizzo – IPMS 3A – Industriale e IPMS 3B – Industriale sono utilizzati per misurare l’occupazione delle Aree del Pavimento in uso esclusivo. Non sono direttamente correlati all’IPMS 1 o all’IPMS 2 – Industriale.
L’SSC ha effettuato ricerche sui mercati immobiliari internazionali ed ha identificato diverse basi di misura che devono essere soddisfatte.
Alcuni mercati richiedono solo una di queste basi di misura per scopi transazionali, essendo l’uso primario previsto per IPMS 3. Altri mercati possono utilizzare l’IPMS 3A – Industriale o l’IPMS 3B – Industriale per la vendita e l’altro per il leasing.
I Fornitori di Servizi non devono semplicemente dichiarare che una misurazione è conforme all’IPMS 3 – Industriale. Il riferimento deve indicare se la misura è IPMS 3A – Industriale o IPMS 3B – Industriale.
Ogni unità in un Edificio multi-occupato deve essere misurata separatamente, ma se conforme, l’Edificio può essere riportato come aggregato dell’IPMS 3A – Industriale o IPMS 3B – Industriale.
IPMS 3A – Industriale
Definizione – IPMS 3A – Industriale è L’Area del Pavimento disponibile in esclusiva per un occupante misurata dalla faccia esterna della Parete Esterna e di eventuali Balconi e comprendente anche eventuali Aree Riparate.
Pratica di misurazione – IPMS 3A – Industriale è misurato sulla faccia esterna della Parete Esterna dell’area in occupazione esclusiva. Nel caso di Edifici annessi o parzialmente annessi, la misurazione viene effettuata sulla linea centrale delle pareti condivise tra gli occupanti.
In assenza di una o più Pareti Esterne, l’IPMS 3A – Industrial (solo a livello del suolo) è misurato sull’Area Coperta, escluse le sporgenze ornamentali e le grondaie oltre le Pareti Esterne.
I muri condivisi con le strutture comuni devono essere misurati in base alla Superficie Finita.
Per quanto riguarda gli avvolgibili e le altre aperture, deve essere seguita la linea perimetrale esterna principale dell’edificio che attraversa tali aperture per misurare l’IPMS 3A – Industrial. Balconi e Mezzanini devono essere misurati fino al bordo esterno della costruzione del pavimento. Se necessario, uffici, magazzini, produzione e altre aree di questo tipo possono essere misurati e dichiarati separatamente.
Misure incluse ma da indicare separatamente – Aree Ausiliarie, Mezzanini e passerelle sono inclusi in IPMS 3A – Industriale, ma devono essere misurati e indicatii separatamente.
La Superficie del Pavimento occupato dalle scale deve essere inclusa solo al livello più basso. Una fossa verticale, la cui apertura nel pavimento e le eventuali pareti circostanti siano inferiori a 0,1m2 (1 ft2) non è identificata separatamente ed è inclusa nella misurazione della Superficie del Pavimento dell’IPMS 3A – Industrial.
Misure escluse ma da indicare separatamente – La misura per IPMS 3A – Industriale non comprende:
– Strutture temporanee
– Pozzi di luce aperti o i vuoti del livello superiore di un atrio
– Scale esterne aperte che non sono parte integrante dell’Edificio, ad esempio, una scala antincendio a struttura aperta
– Qualsiasi struttura al di fuori dell’area coperta
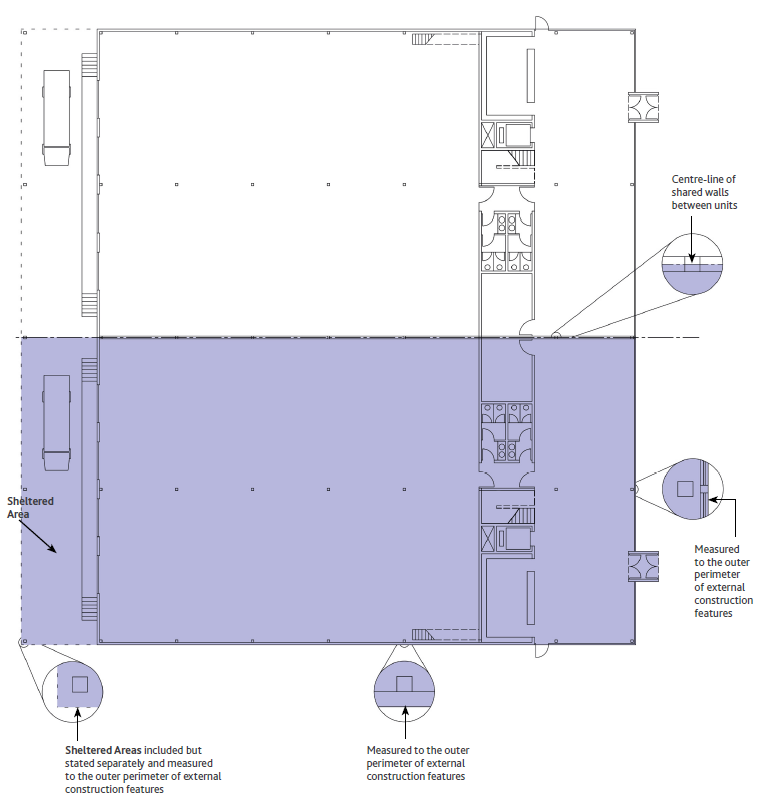
Diagramma 7: IMPS 3A Industriale Piano Terra (Liv. 0)
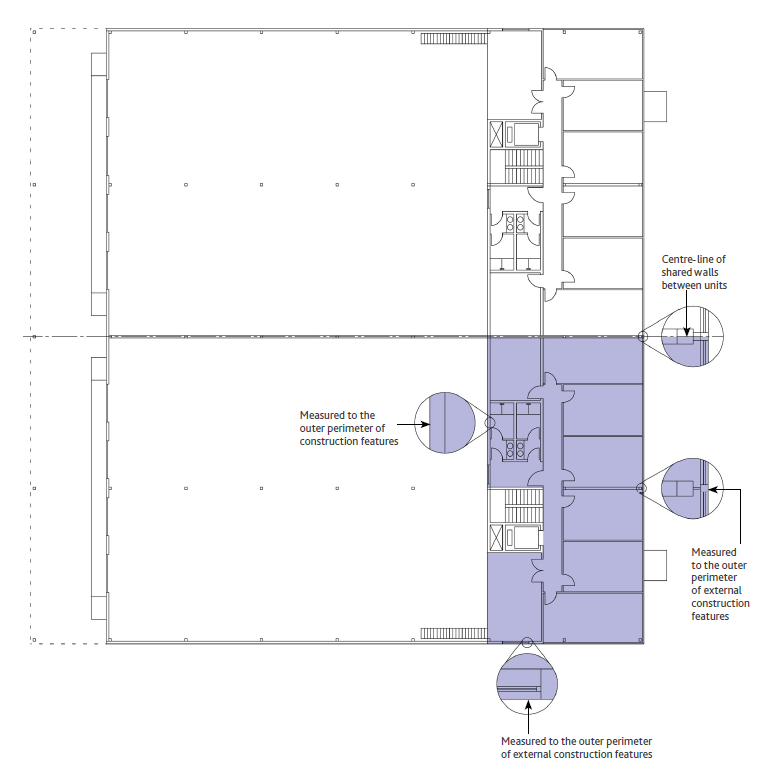
Diagramma 8: IMPS 3A Industriale Piano Sup (Liv. 1)
IPMS 3B – Industriale
Definizione – IPMS 3B – Industriale è L’Area del Pavimento disponibile in esclusiva per un occupante misurata dalla Faccia Dominante Interna delle Pareti Esterne e dei Balconi, o altrimenti della Superficie Coperta.
Pratica di misurazione – Tutte le aree di un Edificio Industriale, compresi ad esempio gli uffici, devono essere misurate in conformità con l’IPMS 3B – Industriale.
Balconi e Mezzanini devono essere misurati sulla faccia interna della balaustra, ma non oltre il bordo esterno della costruzione del pavimento.
Le pareti condivise con le strutture comuni o con gli occupanti adiacenti devono essere misurate sulla Superficie Finita.
La Superficie del Pavimento occupato dalle scale deve essere inclusa solo al livello più basso. Una fossa verticale, la cui apertura nel pavimento e le eventuali pareti circostanti siano inferiori a 0,1m2 (1 ft2) non è identificata separatamente ed è inclusa nella misurazione della Superficie del Pavimento dell’IPMS 3A – Industrial.
Se necessario, l’ufficio, il magazzino, la produzione e altre aree di questo tipo possono essere identificate e misurate e dichiarate separatamente.
Inclusioni – IPMS 3B – Industriale include tutte le aree ad uso esclusivo all’interno della Parete Esterna, inclusi muri interni, colonne e passerelle chiuse o passaggi tra Edifici separati, disponibili per uso diretto o indiretto. Le aree vuote chiuse, come gli atri, sono incluse solo al livello più basso del pavimento.
Misure incluse ma da indicare separatamente – Balconi, Aree di Carico interne e Mezzanini.
Misure escluse ma da indicare separatamente – Le misure per IPMS 3B – Industriale non includono:
– Strutture temporanee
– Qualsiasi area al di fuori della Parete Esterna.
Le aree al di fuori della Parete Esterna, come alcune Aree Ausiliarie, Aree Riparate e Aree di Carico esterne, possono essere misurate e dichiarate separatamente.
Le Aree Riparate devono essere misurate al perimetro esterno della Superficie Coperta e tali misure devono essere indicate singolarmente e separatamente.
 |
 |
| Diagramma 9: IMPS 3B Industriale Piano Terra (Liv. 0) |
Diagramma 10: IMPS 3B Industriale Piano Sup (Liv. 1) |
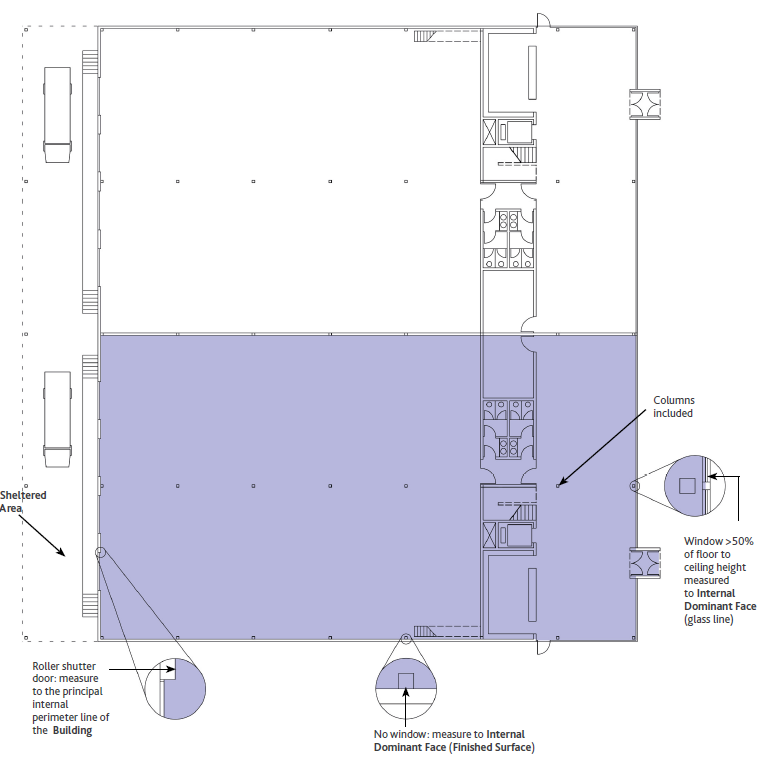
Diagramma 9: IMPS 3B Industriale Piano Terra (Liv. 0)
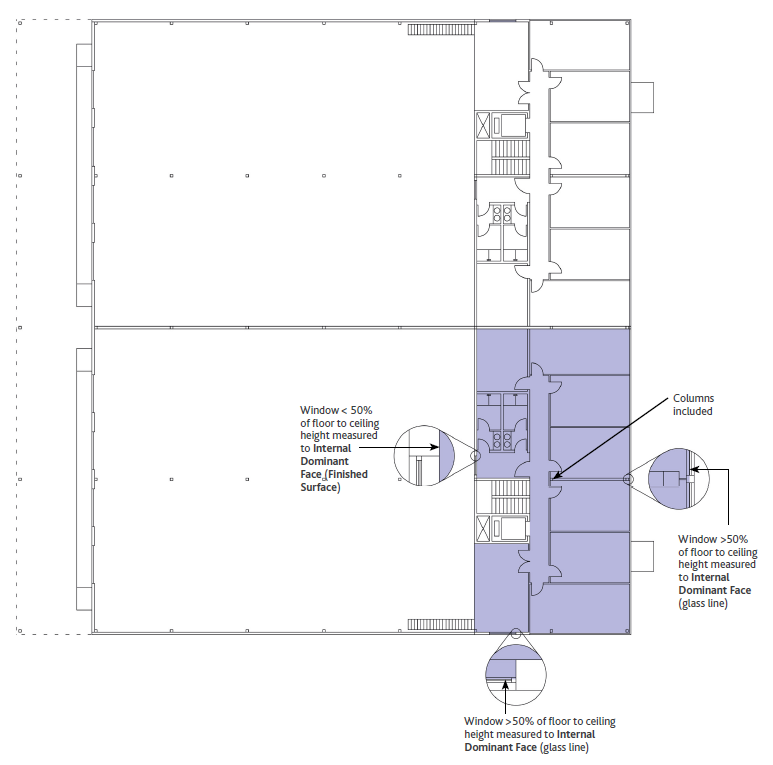
Diagramma 10: IMPS 3B Industriale Piano Sup (Liv. 1)
Tecnica
Faccia Dominante Interna (FDI)
La Faccia Dominante Interna (FDI) è la superficie interna che comprende più del 50% dei primi 2,75 metri misurati verticalmente dal pavimento, o fino al soffitto se inferiore per ogni Sezione di Parete della FDI. In mancanza di elementi diversi la Superficie Finita è considerata l’FDI.
Una Sezione di Parete della FDI è l’estensione di ogni sezione di una Parete Esterna, dove la Superficie Finita interna di ogni parte di una finestra, parete o elemento costruttivo esterno varia dalla Superficie Finita interna della finestra, parete o elemento costruttivo esterno adiacente, ignorando l’esistenza di eventuali colonne.
Se la Faccia Dominante Interna non è verticale, la misura viene effettuata sulla Superficie Finita.
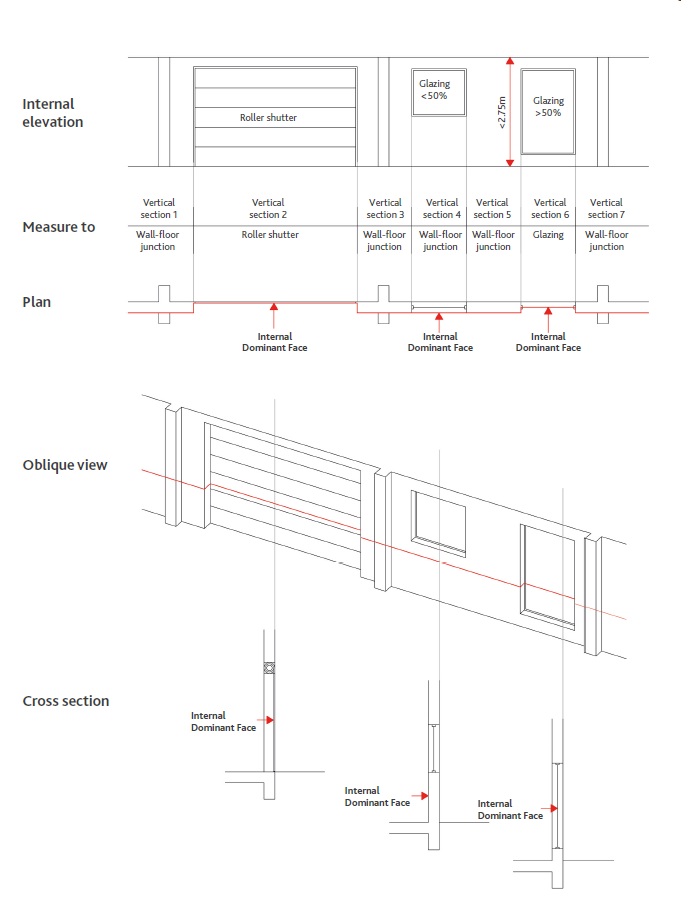
Diagramma 11: Faccia Dominante Interna
Altezza Netta e Altezza Interna
L’Altezza Netta (Clear Height) è l’altezza all’interno di un Edificio o sezione di un Edificio misurata dal pavimento al punto più basso dell’elemento strutturale di copertura, ignorando l’esistenza di staffe, montanti o fissaggi e raccordi.
L’Altezza Interna (Internal Height) è l’altezza all’interno di un Edificio o sezione di un Edificio, misurata dal pavimento al punto più basso di un soffitto, ignorando l’esistenza di eventuali staffe, montanti o fissaggi e raccordi.
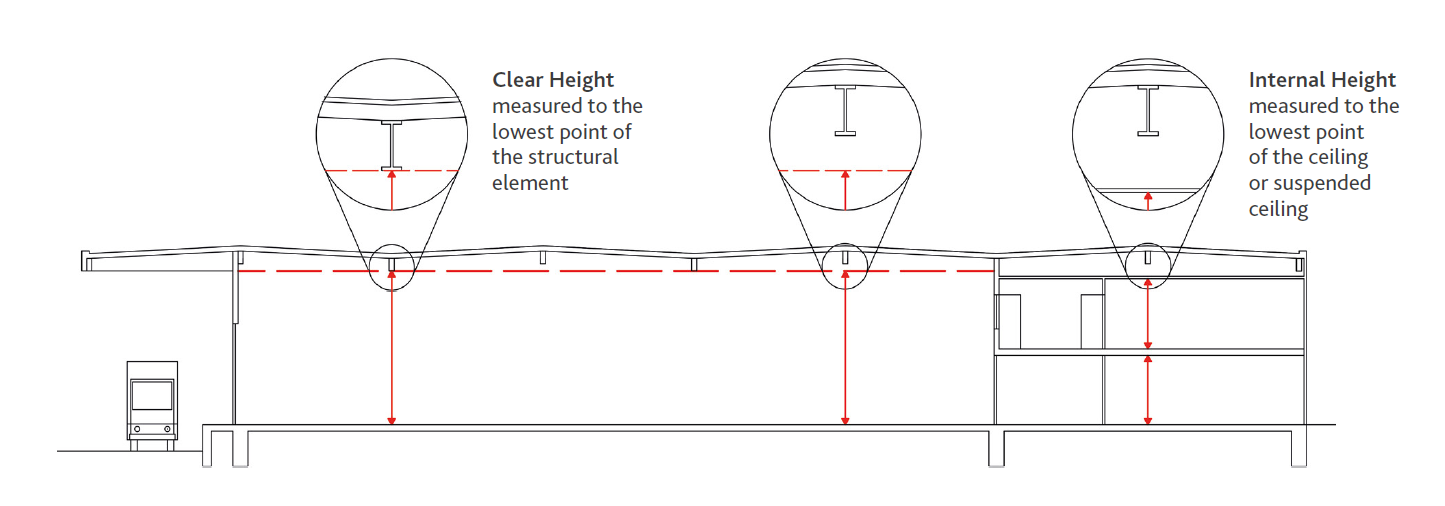
Diagramma 12: Altezza Netta e Altezza Interna
Superficie Coperta
Superficie Coperta (Covered Area) è l’estensione della superficie di un Edificio coperto da uno o più tetti e il cui perimetro è talvolta indicato come la linea di gocciolamento, essendo l’estensione strutturale permanente più esterna, escluse le sporgenze ornamentali.
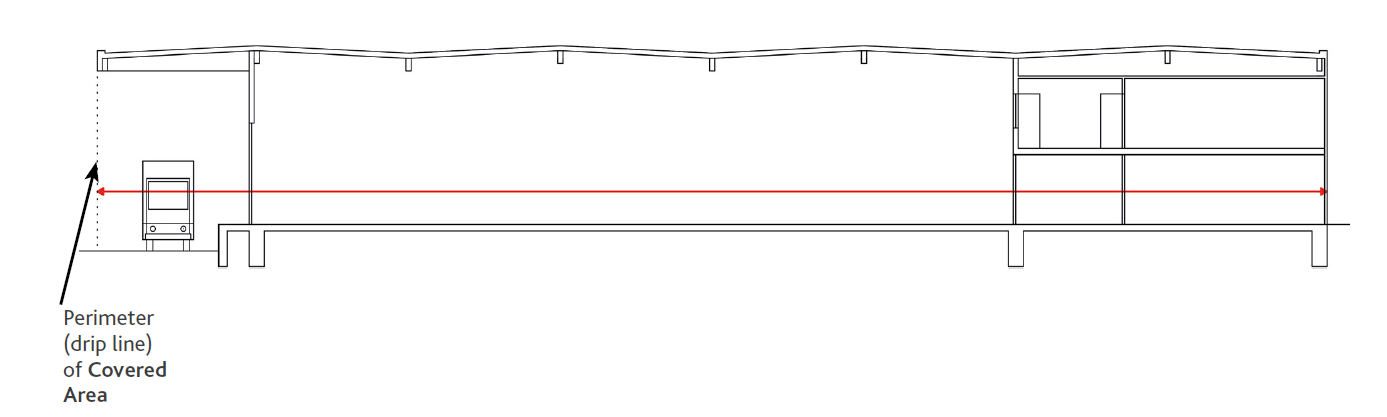
Diagramma 13: Estensione della Superficie Coperta
Muri in comune
Quando un Edificio si estende su più di una Proprietà individuale separata da un muro comune, come nelle unità industriali adiacenti, allora l’IPMS 1 deve essere misurato alla linea centrale del muro comune, a meno che il confine dell’area di proprietà non differisca, nel qual caso l’area di proprietà ha la precedenza.
IPMS Superficie dei Componenti Industriali
Qui di seguito sono consigliate le Superfici dei Componenti industriali che dovrebbero essere utilizzate quando le aree devono essere assegnate separatamente per il costo o altri scopi previsti dall’IPMS 1 e dall’IPMS 2 – Industriale. Questi possono essere ulteriormente suddivisi, se necessario.
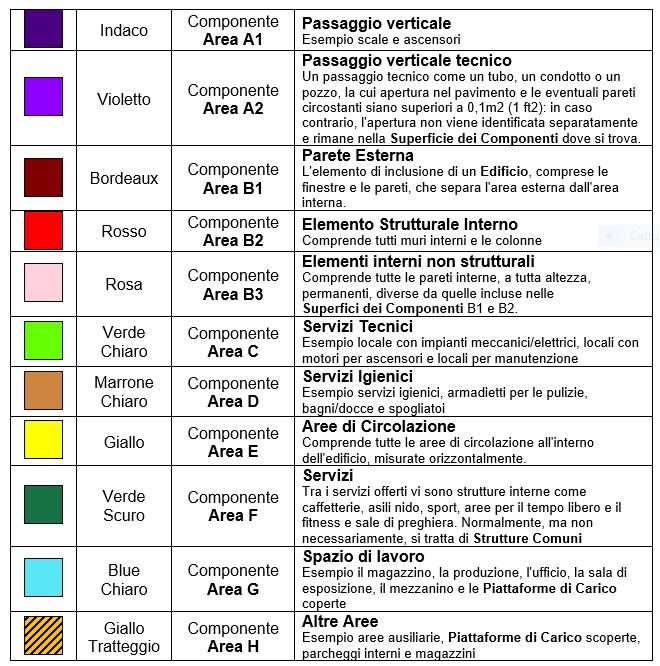
Se uno spazio particolare può essere assegnato a più di una Superficie dei Componenti, allora deve essere assegnato alla Superficie dei Componenti che meglio riflette la sua funzione primaria di progettazione all’interno dello spazio più grande.
Le Superfici dei Componenti, nel loro insieme o in parte, possono essere classificate come private (essendo riservate esclusivamente ad un solo occupante) o condivise (essendo disponibili per l’uso di più occupanti).
Le aree all’interno della Superficie dei Componenti H non disponibili per uso industriale diretto possono essere descritte come ausiliarie. Esse devono essere misurate, ma possono anche essere dichiarate in modo alternativo. Ad esempio, i parcheggi possono essere indicati anche in base al numero di posti.
Aree ad uso limitato
Le aree a uso limitato, sono incluse nelle aree segnalate IPMS, ma devono essere identificate, misurate e dichiarate separatamente.
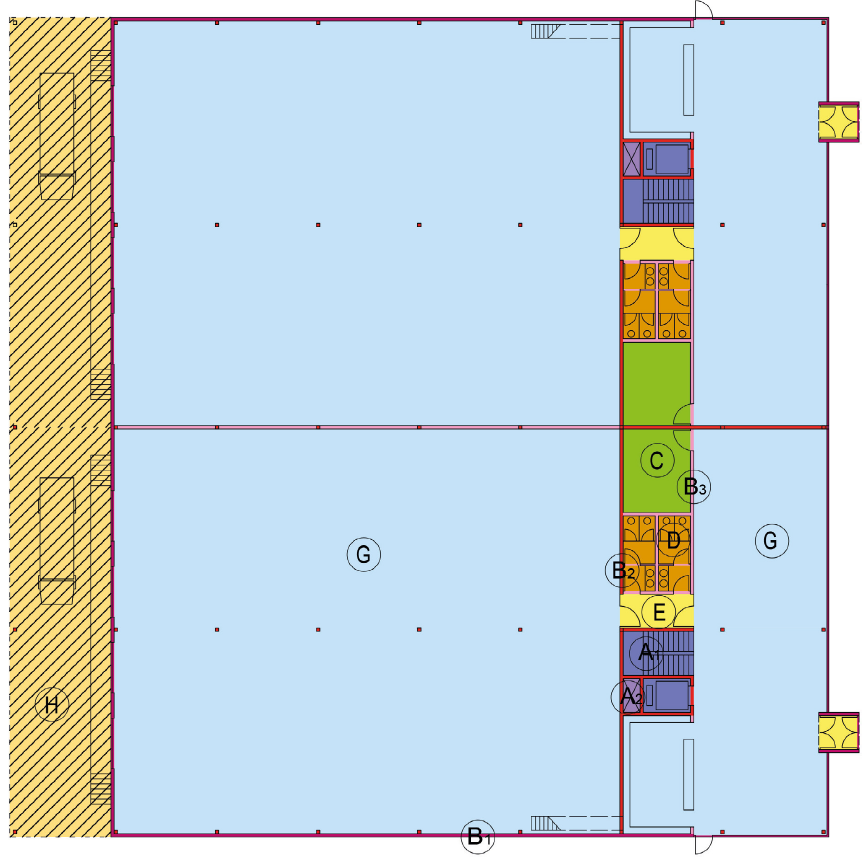
Diagramma 14: IPMS – Industriale – Piano Terra (Liv. 0) – Superficie dei Componenti
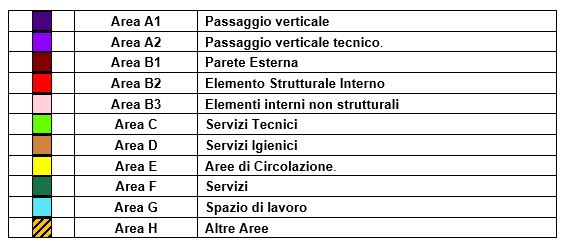
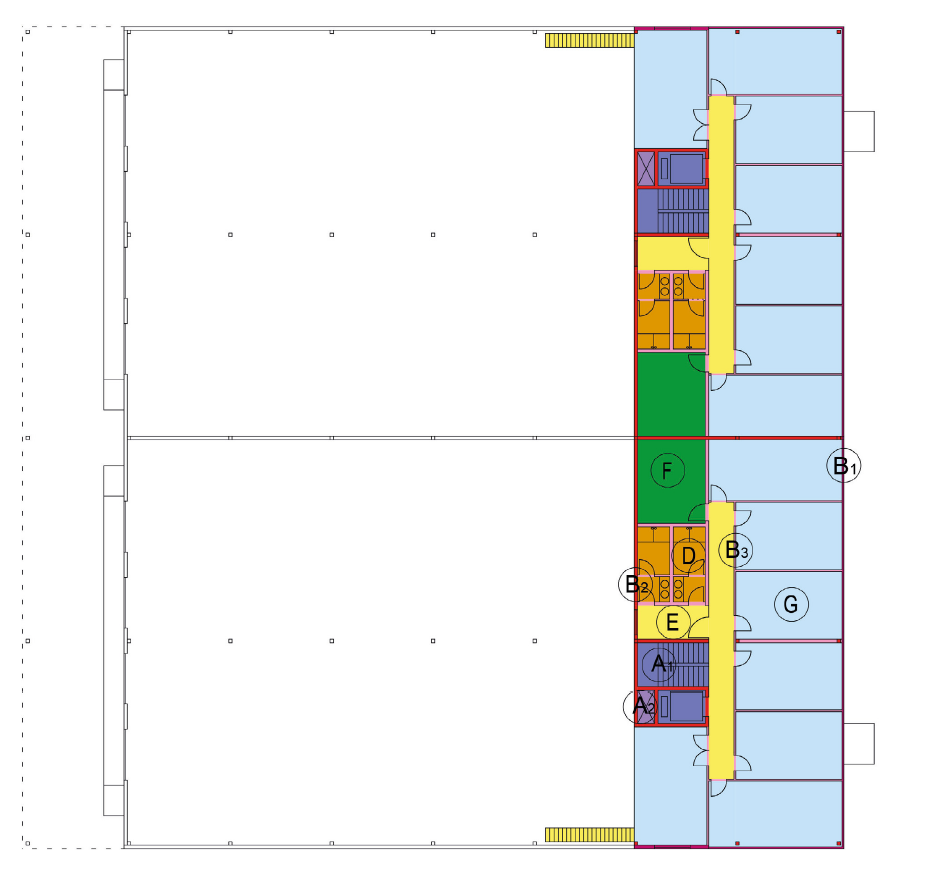
Diagramma 15: IPMS – Industriale – Piano Superiore (Liv. 1) – Superficie dei Componenti

Esempio di tabella per la Superficie dei Componenti
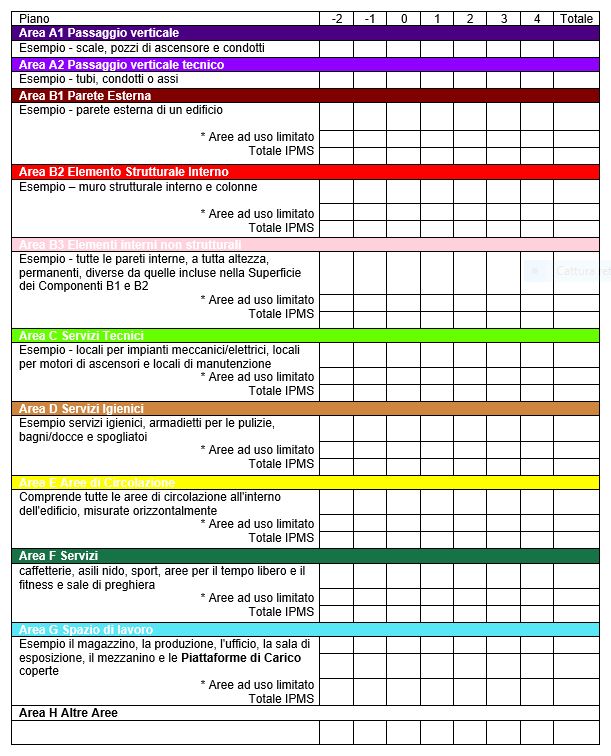
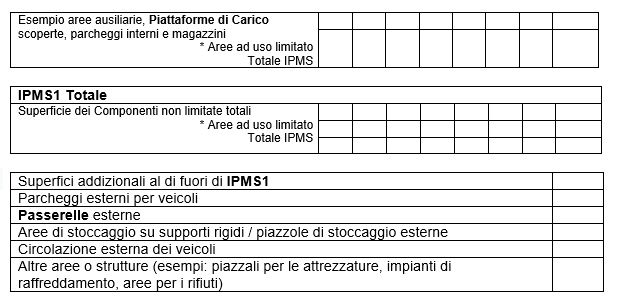
Tutti i sottocomponenti devono essere indicati separatamente.
* Ogni eventuale limitazione deve essere indicata separatamente.
** L’entità di ogni utilizzo all’interno dell’Area Componente H deve essere indicata separatamente.
Fonti:
www.ipmsc.org
 Pasquale Marottoli – ZEDPROGETTI srl
Pasquale Marottoli – ZEDPROGETTI srl
After the article “THE IPMS STANDARD FOR THE MEASUREMENT OF OFFICE BUILDINGS”, we continue the discussion taking into account the measurement of industrial buildings
The IPMS standard for measuring units was created in order to make the unit measurement system unique, so that the data can be read internationally. The International Property Measurement Standards Coalition (IPMSC) was formed on May 30, 2013 after meeting at the World Bank in Washington DC. The Coalition, which comprises 87, aims to achieve the harmonization of national property measurement standards through the creation and adoption of agreed international standards for the measurement of buildings.
This document for the measurement of industrial buildings is the third construction class standard prepared by the Coalition Standard Setting Committee (SSC).
With regard to “IPMS: Buildings for Industrial Use”, 4 standards have been defined
– IPMS 1 – standard for measuring the total area of buildings, for planning activities or for estimating construction costs and which is assumed to be valid for all categories of buildings.
– IPMS 2 – Industrial was developed to measure the internal areas of an industrial building complex and, with the use of the Component Areas, will help the real estate industry to make efficient use of space and for reference data.
– IPMS 3A – Industrial and IPMS 3B – Industrial used to measure areas of exclusive occupation for transactions and other purposes. The SSC has identified two different measurement bases, necessary to meet the needs of the global market for measuring exclusive occupancy areas.
There are some basic definitions that cover the elements covered.
Definitions
– Internal Height – The height inside a Building or section of a Building, measured from the floor to the lowest point of a ceiling, ignoring the existence of any brackets, uprights or fixings and fittings.
– Net Height – The height inside a Building or section of a Building measured from the floor to the lowest point of the structural roof element, ignoring the existence of brackets, posts or fixings and fittings.
– Auxiliary Area – An area of exclusive use, which is detached from the main measured area or used for additional purposes.
– Loading Area – Areas designed for vehicle access near a Loading Platform.
– Floor Area – The area of a normally horizontal, permanent, load-bearing structure on each level of a building.
– Sheltered Area – Any part of the Covered Area not completely enclosed, but excluding insignificant areas under the gutters.
– Balustrade – A protective barrier formed by a solid wall, railings or other structures.
– Balcony – An external platform on the upper floor with a balustrade on the open sides protruding or recessed from an external wall and which includes in this definition, generally accessible panoramic terraces, external galleries and loggias.
– Coalition – The administrators of the IPMS, which includes non-profit organizations, each with a public interest mandate.
– Component – One of the main elements into which the Floor Area of a building can be divided.
– Building – An independent connected or detached structure that forms all or part of a property.
– Industrial Building – A building used primarily for industrial purposes such as production and storage, regardless of whether or not part of the building is used for other purposes.
– Space Measurement Expert – A Service Provider qualified by experience or training to measure Buildings in accordance with the IPMS standard.
– Interior Dominating Face (IDF) – The interior surface area comprising more than 50% of the first 2.75 meters measured vertically from the floor, or to the ceiling if lower in height, for each IDF Wall Section. If this does not occur, the finished surface is considered the IDF.
– Service Provider – Any entity that provides real estate consulting to a User or Third Party, including but not limited to Evaluators, Inspectors, Facility Managers, Property Managers, Asset Managers, Agents and Brokers, Space Measurement Experts, Cost Consultants, Interior Designers and Architects.
– Real Estate Industry – Includes Users, Service Providers and Third Parties.
– IPMS – International Property Measurement Standards.
– IPMSC – The International Property Measurement Standards Coalition.
– IPMS 1 – The total surfaces of each floor of a Building measured at the external perimeter of the Exterior Walls, Covered Areas and Balconies.
– IPMS 2 – The total surfaces of each floor of a Building measured at the Internal Dominating Face of all Exterior Walls and Balconies on each floor.
– IPMS 3 – The Floor Area available exclusively for one occupant.
– Mezzanine – An intermediate or partial floor, other than a walkway, which is usually fully or partially open on one or more sides.
– Patio – A paved or paved terrace, adjacent to a Building, which can be covered by an independent structure.
– External Wall – The element of inclusion of a Building, including windows and walls, that separates the external area from the internal area.
– Walkway – An internal or external walkway above the surrounding area that provides access to the upper level.
– Loading Platform – Platforms elevated to the opening of a building designed for receiving or shipping goods or equipment.
– Property – Any real estate resource within a building.
– IDF Wall Section (interior dominant face) – The extent of any section of an exterior wall where the finished interior surface of any part of a window, wall or other exterior construction feature varies from the adjacent finished interior surface of the window, wall or exterior construction feature, ignoring the existence of any columns.
– SSC – The Standard Setting Committee appointed by the IPMSC to develop global standards for measuring properties.
– Structure – A construction that provides shelter or performs an ancillary function, but is not necessarily completely enclosed.
– Common Facilities – Those parts of a building that, in multiple occupations, would provide shared facilities that generally do not change over time and may include, for example, traffic areas, stairs, escalators, elevators/elevators, engine rooms, toilets, cleaning cabinets, plant rooms, fire shelter areas, maintenance rooms and unassigned parking spaces.
– Standard Facilities – see Common Facilities.
– Temporary Structure – A physical element within a temporarily or permanently installed building whose removal would not damage the physical integrity of the Building.
– Component Area – The total Floor Area allocated to one of the Components.
– Covered Area – The surface area of a Building that is covered by one or more roofs and whose perimeter is sometimes referred to as the drip line, being the outermost permanent structural extension, excluding ornamental protrusions.
– Finished Surface – The surface of the wall directly above the horizontal wall-to-floor intersection, ignoring skirting boards, cable ducts, heating and cooling units, and piping.
– Third – Any entity other than a User or Service Provider with an interest in measuring property, including, but not limited to, governments, banks, other proprietary financial institutions, data analysts and researchers.
– User – An owner-occupier, developer, investor, buyer, seller, owner or tenant.
– Evaluator – A Service Provider with an appropriate professional qualification in evaluation or appraisal.
– Veranda – An open or partially enclosed area outside a Building at ground level (level 0) and covered by a roof that is an integral part of the Building.Purpose and scope of the standards
Purpose of the standards
The objective of the IPMS is to provide transparency in the measurement of Buildings. The IPMS supports requests from Service Providers, Third Parties and Property Users for consistency in reporting the measurement. So far the area declared in identical buildings varies greatly from one country to another and sometimes within the same country due to different measurement conventions.
Measurements can be used for asset management, comparison, construction, facility management, marketing, real estate financing, research, transaction, valuation and other purposes.Use of Standards
IPMS defines what is to be measured in a Building and the measurement parameters. The IPMS does not dictate how measurements are to be obtained or used.
The appropriate IPMS standard (e.g. office, residential, industrial, commercial) to be used must be chosen based on the current or proposed function of the Building or part of Building to be measured.
IPMS may be used for any purpose agreed between Users, Service Providers and Third Parties.
IPMS provides a common language that can interface with existing local measurement standards.Accuracy
Service Providers shall adopt appropriate measurement and calculation processes to meet Users’ needs. These requirements may vary from a broad approximation for certain purposes to a precise calculation for contractual or other reasons.1.4 Floor level designation
The SSC found that there is no market coherence in the reference to a certain level.
For all property classes IPMS has adopted level 0 as the primary baseline level. Upper and lower levels are referred to sequentially as the number of levels above or below Level 0. For example, levels 1, 2 or 3, etc. are above Level 0 and levels -1, -2 or -3, etc. are below Level 0.General Measurement and Calculation Criteria
– The property must be measurable.
– The measurement must be verifiable according to objective criteria.
– All measurements, except for heights, shall be taken horizontally.
– Measurements and calculations shall be clearly documented, specifying the following information:
o The IPMS standard adopted, e.g. IPMS 1, IPMS 2 – Industrial or IPMS 3A – Industrial or IPMS 3B – Industrial
o The criterion used for the measurement
o The unit of measurement
o Measurement tolerance
o The date of measurement.
– Buildings must be measured individually and reported floor by floor as existing or proposed at the time of measurement.
– IPMS principles should be extrapolated using a common sense approach.Good measurement practice
– General – The SSC recommends that all IPMS measurements be accompanied by CAD (computer-aided design) or BIM (building information modelling) data, but where other drawings are used as a basis for measurement, it will be preferable to use the dimensions shown on the drawings rather than relying solely on those measured. The Service Provider must explain how the Floor Area is determined, for example from CAD drawings, other drawings or by laser or metric tape measurement.
– Units of Measurement – Measurements and calculations must be made in the units of measurement commonly used in the respective country. Users and third parties may request to convert measurements, in which case the conversion factor must be indicated.
– Measurement Reports – Any Component Area in IPMS 1 or IPMS 2 reported to a User or Third Party should, where possible and where appropriate, be referred to a drawing and a properly coloured Component Area spreadsheet. When reporting measurements and plan areas for proposed developments, Service Providers shall take particular care to ensure that measurements are cross-referenced with the highest possible accuracy with respect to projects at the date of the report.
– Limited Areas of Use – Service Providers should be aware that in some markets there may be areas of the buildings that cannot be legally or effectively occupied due to local or national legislation. These areas and their limitations must be identified, measured and reported separately within the IPMS reported areas. If the areas are subject to restrictions, this shall be declared in the reporting document and in any component area spreadsheet. Users and Third Parties should be aware that the inclusion of measured areas in the IPMS does not necessarily mean that the areas are available for occupation or legal use. The reason why a particular area is considered a Restricted Use Area should be indicated. The following examples are not exhaustive:
o Example 1 – Area Difference from the Domestic Dominant Face. It may be necessary to show the difference, if applicable, in the floor area between the measurements taken on the Interior Dominant Face and the measurements taken on the wall-floor junction.
o Example 2 – Areas with height restrictions
In several markets, defined areas of limited or restricted height are identified separately. This height may vary from one jurisdiction to another and in some cases the limited height may be due to construction features.o Example 3 – Areas with limited natural light
In some jurisdictions, areas with limited natural light in a Building must be identified separately.o Example 4 – Above and below ground
A building is generally composed of floors above ground and basement floors. For measurement purposes, this distinction may be important to determine the conditions under which the premises may be used in accordance with local or national legislation, rules on fitness for habitation or taxation.
– Adaptation between IPMS and other standards
If dual reporting is adopted, the correspondence between the IPMS and the standard referred to must be properly explained. The CSS recommends that Coalition members provide interface guidance in their local implementation procedures for their members.IPMS Standard
IPMS standards (and their main uses) are:
– IPMS 1 (External)
– IPMS 2 – Industrial (indoor)
– IPMS 3A – Industrial (external: exclusive employment)
– IPMS 3B – Industrial (domestic: exclusive employment).IPMS 1
Use – IPMS 1 is used to measure the area of a building, including external walls. The primary intent of IPMS 1 is to be used for planning purposes or for the summary cost calculation of development proposals.
IPMS is the measurement of the whole building.Definition – IPMS 1: The total area of each floor level of a Building measured at the outer perimeter of the Outer Walls, Sheltered Areas and Balconies.
The definition for IPMS 1 is the same for all Building classes.
In many markets, but not universally, this is known as the Gross External Area.Measurement Practice – Areas for IPMS 1 must be taken from drawings or on site. If necessary, IPMS 1 can be reported Component by Component for each floor of a Building. The sum of the Component Surfaces must be equal to IPMS 1.
If there are no drawings available for a basement, the area must include an estimate of the thickness of the exterior walls.
For Sheltered Areas, IPMS 1 must be measured at the Covered Area. For Rolling shutters and other openings, IPMS 1 must be measured by following the main outer perimeter line of the building through these openings.
Balconies and mezzanines shall be measured to the outer edge of the floor construction.Inclusions – IPMS 1 includes all areas and walls, columns and passageways or closed passages between separate buildings, available for direct or indirect use. Empty closed areas, such as atria, are only included at the lowest level of the floor.
Measures included but to be stated separately -Balconies, Sheltered Areas, Verandas and Mezzanines are included, but the size of each must be stated separately.
Measurements excluded but to be reported separately – Measurement for IPMS 1 is not included:
– Temporary structures
– Open light wells or the voids of the upper level of an atrium
– Open external stairs that are not an integral part of the building, e.g. an open structure fire ladder
– Any structure outside the covered area.
IPMS 2 – IndustrialUse – IPMS 2 – Industrial is a measure of the entire building that is used to measure the internal boundary area of a building. The primary intended use is to provide data on space use and for comparison. IPMS 2 – Industrial allows Users, Third Parties and Service Providers to directly compare data from different market practices.
Definition – IPMS 2 – Industrial is The total surface area of each floor level of a building measured at the Internal Dominating Face of all exterior walls and balconies on each level.
In many markets, but not universally, this is similar to the gross interior area.Measurement practice – All areas of an industrial building, including for example offices, must be measured in accordance with IPMS 2 – Industrial.
Balconies and mezzanines must be measured up to the inner face of the balustrade, but not beyond the outer edge of the floor construction.
If required, IPMS 2 – Industrial can be reported Component by Component for each floor of a Building.Inclusions – IPMS 2 – Industrial includes all interior areas, including interior walls and columns. Empty enclosed areas, such as atria, are included only on the lowest level of the floor.
Measurements included but to be stated separately – Balconies, Internal Loading Areas, Mezzanines and walkways or closed passageways between separate buildings, available for direct or indirect use, are included but the size of each must be stated separately.
Measurements excluded but to be stated separately – Areas outside the Outer Wall, such as sheltered areas and External Loading Areas, are not to be measured but if they are measured, these areas must be declared individually and separately.
Sheltered Areas must be measured at the finished surface of any wall and otherwise at the outer perimeter of the covered area.
IPMS 3 – IndustrialUse – IPMS 3A – Industrial and IPMS 3B – Industrial are used to measure occupancy of Floor Areas in exclusive use. They are not directly related to IPMS 1 or IPMS 2 – Industrial.
The SSC has carried out research on international real estate markets and has identified several measurement bases that need to be met.
Some markets require only one of these measurement bases for transactional purposes, the primary intended use being IPMS 3. Other markets may use IPMS 3A – Industrial or IPMS 3B – Industrial for sale and the other for leasing.
Service Providers do not simply have to declare that a measurement complies with IPMS 3 – Industrial. The reference must indicate whether the measurement is IPMS 3A – Industrial or IPMS 3B – Industrial.
Each unit in a Multi-Occupied Building shall be measured separately, but if compliant, the Building may be reported as an aggregate of IPMS 3A – Industrial or IPMS 3B – Industrial.IPMS 3A – Industrial
Definition – IPMS 3A – Industrial is the Floor Area available exclusively for an occupant measured from the outer face of the Outer Wall and any Balconies and also includes any Sheltered Areas.
Measurement Practice – IPMS 3A – Industrial is measured on the outer face of the Outer Wall of the exclusive occupancy area. In the case of adjoining or partially adjoining buildings, the measurement is carried out on the central line of the walls shared between the occupants.
In the absence of one or more Outer Walls, IPMS 3A – Industrial (ground level only) is measured on the Covered Area, excluding ornamental protrusions and gutters beyond the Outer Walls.
Walls shared with common structures must be measured on the Finished Area.
As far as roller shutters and other openings are concerned, the main external building perimeter line through these openings must be followed to measure IPMS 3A – Industrial. Balconies and mezzanines must be measured to the outer edge of the floor construction. If necessary, offices, warehouses, production and other such areas may be measured and declared separately.Measurements included but to be reported separately – Auxiliary Areas, Mezzanines and walkways are included in IPMS 3A – Industrial, but must be measured and reported separately.
Floor area occupied by stairs should only be included at the lowest level. A vertical pit, whose opening in the floor and any surrounding walls are less than 0.1m2 (1 ft2) is not separately identified and is included in IPMS 3A – Industrial Floor Area measurement.Measures excluded but to be indicated separately – The measure for IPMS 3A – Industrial does not include:
– Temporary structures
– Open light wells or the voids of the upper level of an atrium
– Open external stairs that are not an integral part of the building, e.g. an open structure fire ladder
– Any structure outside the covered area
IPMS 3B – IndustrialDefinition – IPMS 3B – Industrial is the Floor Area available exclusively for an occupant measured by the Internal Dominating Face of the External Walls and Balconies, or otherwise of the Covered Surface.
Measurement Practice – All areas of an Industrial Building, including for example offices, must be measured in accordance with IPMS 3B – Industrial.
Balconies and Mezzanines must be measured on the inner face of the balustrade, but not beyond the outer edge of the floor construction.
Walls shared with common facilities or adjacent occupants must be measured on the Finished Surface.
The Floor Area occupied by stairs should only be included on the lowest level. A vertical pit, whose opening in the floor and any surrounding walls are less than 0.1m2 (1 ft2) is not separately identified and is included in the IPMS 3A – Industrial Floor Area measurement.
If necessary, the office, warehouse, production and other such areas can be identified and measured and declared separately.Inclusions – IPMS 3B – Industrial includes all areas of exclusive use within the Outer Wall, including interior walls, columns and closed walkways or walkways between separate buildings, available for direct or indirect use. Empty closed areas, such as atria, are included only at the lowest floor level.
Measurements included but to be indicated separately – Balconies, Internal Loading Areas and Mezzanines.
Measurements excluded but to be indicated separately – Measurements for IPMS 3B – Industrial are not included:
– Temporary Structures
– Any area outside the Outer Wall.
Areas outside the Outer Wall, such as some Auxiliary Areas, Sheltered Areas and External Loading Areas, can be measured and declared separately.
Sheltered Areas must be measured at the outer perimeter of the Covered Area and such measurements must be reported individually and separately.
TechniqueInternal Dominant Face (IDF)
The Internal Dominating Face (IDF) is the internal surface area that includes more than 50% of the first 2.75 meters measured vertically from the floor, or to the ceiling if lower for each IDF Wall Section. In the absence of other elements the Finished Surface is considered the IDF.
An IDF Wall Section is the extension of each section of an External Wall, where the Internal Finished Surface of each part of a window, wall or external construction element varies from the Internal Finished Surface of the adjacent window, wall or external construction element, ignoring the existence of any columns.
If the Internal Dominating Face is not vertical, the measurement is made on the Finished Surface.Net Height and Internal Height
Clear Height is the height inside a Building or section of a Building measured from the floor to the lowest point of the structural roof element, ignoring the existence of brackets, uprights or fixings and fittings.
Internal Height is the height inside a Building or section of a Building, measured from the floor to the lowest point of a ceiling, ignoring the existence of any brackets, uprights or fixings and fittings.
Covered SurfaceCovered Area is the extension of the surface area of a building covered by one or more roofs and whose perimeter is sometimes referred to as the drip line, being the outermost permanent structural extension, excluding ornamental projections.
Common wallsWhen a Building extends over more than one Individual Property separated by a common wall, as in adjacent industrial units, then IPMS 1 must be measured at the centre line of the common wall, unless the boundary of the property area differs, in which case the property area takes precedence.
IPMS Industrial Components Area
The following are recommended Industrial Component Surfaces that should be used when areas are to be allocated separately for cost or other purposes under IPMS 1 and IPMS 2 – Industrial. These can be further subdivided if necessary.Indigo Component
Area A1 Vertical passage
Example stairs and elevators
Violet Component
Area A2 Technical vertical passage
A technical passage such as a pipe, duct or well, whose opening in the floor and any surrounding walls is greater than 0.1m2 (1 ft2): otherwise, the opening is not separately identified and remains in the Component Area where it is located.
Bordeaux Component
Area B1 External Wall
The element of inclusion of a Building, including windows and walls, that separates the outside area from the inside area.
Red Component
Area B2 Internal Structural Element
Includes all interior walls and columns
Pink Component
Area B3 Non-structural internal elements
Includes all interior walls, full-height, permanent, other than those included in the
Surfaces of Components B1 and B2.
Light Green Component
Area C Technical Services
Local example with mechanical/electrical systems, rooms with lift motors and maintenance rooms
Light Brown Component
Area D Toilets
Example toilets, cleaning cabinets, bath/showers and changing rooms
Yellow Component
Area E Circulation Areas
Includes all circulation areas within the building, measured horizontally.
Dark Green Component
Area F Services
Among the services offered are indoor facilities such as cafeterias, kindergartens, sports, leisure and fitness areas and prayer rooms. Normally, but not necessarily, these are Common Facilities
Light Blue Component
Area G Workspace
Example of warehouse, production, office, exhibition hall, mezzanine and covered loading platforms
Yellow
Hatch Component
Area H Other Areas
Example of auxiliary areas, outdoor loading platforms, indoor car parks and warehousesIf a particular space can be assigned to more than one Component Area, then it must be assigned to the Component Area that best reflects its primary design function within the larger space.
Component Surfaces, as a whole or in part, may be classified as private (being reserved for one occupant only) or shared (being available for use by multiple occupants).
Areas within the Component Surface H not available for direct industrial use can be described as auxiliary. They must be measured, but can also be declared in an alternative way. For example, parking spaces may also be indicated by the number of spaces.Restricted use areas
Restricted use areas are included in the IPMS reported areas, but must be identified, measured and declared separately.

